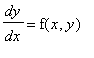
Lecture 8
Text: Sections 1.3, 1.4
Direction Fields. A useful technique that can be used to visualize solutions of the first order DE
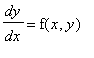
is the use of the direction field of the equation which consists of a short line segment of slope f(x,y) centered at the point (x,y). For example,
![[Maple Plot]](images/lecture82.gif)
is the direction field of the differential equation
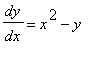 .
.
Using this direction field one can sketch solutions of the DE. For example, the solution with y(0)=.5 has the graph
![[Maple Plot]](images/lecture84.gif)
A systematic way to construct the direction field is to draw a short line segment of slope m at various points of the curve f(x,y)=m for a selected range of values of m. These curves are the isoclines for the differential equation
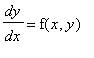 . For the above DE the isoclines are the curves
. For the above DE the isoclines are the curves
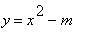 .
.
The Phase Line.
The first order DE
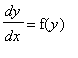 is called
autonomous
since the independent variable does not appear explicitly. The isoclines are made up of horizonal lines y=f(m). The DE has the constant solution y=m if and only if f(m)=0. These values of m are the
equilibrium or stationary points
of the DE.
The equilibrium point y=m is called a
source
if f(y) changes sign from - to + as y increases from just below y=m to just above y=m and is called a
sink
if f(y) changes sign from + to - as y increases from just below y=m to just above y=m; it is called a
node
if there is no change in sign.Solutions y of the DE appear to be attracted by the line the line y=m if m is a sink and move away if m is a source. The y-axis on which is plotted the equilibrium points of the DE with arrows between these points to indicate when the solution y is increasing or decreasing is called the
phase line
of the DE.
is called
autonomous
since the independent variable does not appear explicitly. The isoclines are made up of horizonal lines y=f(m). The DE has the constant solution y=m if and only if f(m)=0. These values of m are the
equilibrium or stationary points
of the DE.
The equilibrium point y=m is called a
source
if f(y) changes sign from - to + as y increases from just below y=m to just above y=m and is called a
sink
if f(y) changes sign from + to - as y increases from just below y=m to just above y=m; it is called a
node
if there is no change in sign.Solutions y of the DE appear to be attracted by the line the line y=m if m is a sink and move away if m is a source. The y-axis on which is plotted the equilibrium points of the DE with arrows between these points to indicate when the solution y is increasing or decreasing is called the
phase line
of the DE.
The autonomous DE
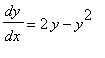 has 0 and 1 as equilibrium points. The point y=0 is a source and y=2 is a sink. The direction field of this DE is
has 0 and 1 as equilibrium points. The point y=0 is a source and y=2 is a sink. The direction field of this DE is
![[Maple Plot]](images/lecture89.gif)
This DE is a logistic model for a population having 2 as the size of a stable population. If the population is reduced at a constant rate s>0, the DE becomes
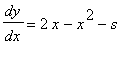 .
.
which has a source at the larger of the two roots of the equation
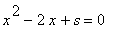 for s<2. If s>2 there is no equilibrium point and the popuation dies out as y is always decreasing. The point s=2 is called a
bifurcation point
of the DE.
for s<2. If s>2 there is no equilibrium point and the popuation dies out as y is always decreasing. The point s=2 is called a
bifurcation point
of the DE.